tests to see if you have a rotator cuff tear|how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff : chain store Diagnosing a rotator cuff tear involves a comprehensive review of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests like MRI or . WEB10 horas atrás · Meteorologists predict as much as 10 feet (3 meters) of snow is possible in the mountains around Lake Tahoe by the weekend, with 3 to 6 feet (0.9 to 1.8 meters) .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB1 de jun. de 2021 · 188K views 1 year ago. Link de download no comentário fixado.Download link in the comment attached.Enlace de descarga en el comentario adjuntoCanal do meu .
Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as .
A doctor or physiotherapist can use one of more than 25 functional tests during a physical exam to diagnosis a torn rotator cuff. .Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic imaging study such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear may prevent symptoms such as .
Diagnosing a rotator cuff tear involves a comprehensive review of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests like MRI or . Doctors can diagnose a torn rotator cuff by doing a physical examination, ultrasound, x-ray or MRI. These exams will help them determine the severity of the tear. Pain from a torn rotator.
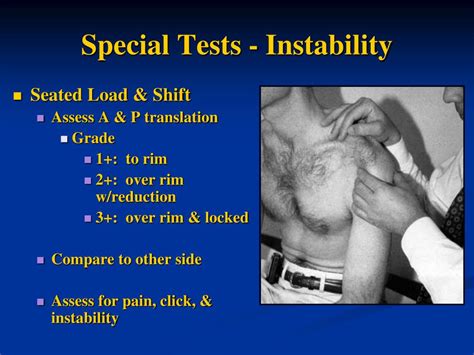
Lift Off Test. This test specifically tests for scapular instability or for a lesion of the subscapularis muscle. In this test, you begin by placing the injured arm behind your back, with the back of your hand resting on your mid lumbar . Rotator cuff tear test. There are many special tests doctors use to diagnose rotator cuff tear. Although they are not always reliable, you likely have a rotator cuff tear if you feel pain when .Rotator cuff injuries are among the most common causes of shoulder pain. These can manifest as bursitis, tendonitis or tendon tears. The patients usually complain of pain and reduced function of the affected shoulder. In young .A rotator cuff may tear partly or fully. What causes a rotator cuff injury? Injury and degeneration are the two main causes of rotator cuff tears. An injury to the rotator cuff, such as a tear, may happen suddenly when falling on an outstretched hand. It may also develop over time due to repetitive activities.
Learn about the 3 ways to test for a rotator cuff tear from Dr. Arlan Alburo of Orthopedic & Balance Therapy Specialists.If you are located in Northwest Indi.
Rotator cuff tears cause shoulder pain that can make even the most simple daily tasks painful – like reaching for a bottle of shampoo in the shower. So if you have shoulder pain, how do you know specifically whether or not it is a rotator cuff tear? Here are 3 simple home tests you can use to check and see if you’ve torn your rotator cuff .Clinical examination (see 9. Examination): active and passive range of motion, strength tests and rotator cuff tests . To enhance the ability to detect full-thickness rotator cuff tears, a test-item cluster has been developed. A cluster improves the post-test probability for the clinical diagnosis of a full-thickness tear. If we suspect you have a torn rotator cuff, we'll need to know whether it's a total or partial tear. An MRI exam will allow us to see inside your shoulder and analyze the bone, muscle, and connective tissues. This information helps us determine what type of treatment might benefit you most. For small to moderate tears, physical therapy may .
As a rotator cuff tear becomes larger, retracted, and more degenerative in nature, the patient’s shoulder dysfunction will become more apparent as it becomes difficult for the rotator cuff as a group to function well. Shoulder Shrug Sign. The first special test I perform to diagnose a rotator cuff tear is the shoulder shrug sign.
Depending on the symptoms you describe, the physical examination will involve one or more rotator cuff injury tests to locate areas of tenderness, evaluate the range of motion, and determine the movements which cause pain and weakness. If tests suggest a rotator cuff injury, imaging may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . Empty Can Test; Full Can Test; Rotator cuff tear (Supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles) and shoulder impingement External Rotation Lag Sign; Rotator cuff tear (Subscapularis)The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as: Drop Arm Test. This simple test assesses the possibility of a rotator cuff tear. During the test, the patient (either sitting or standing) holds their arm straight out at a 90 degree angle, then slowly lowers the arm down to their side. The provider is looking for the patient’s ability to raise and lower the arm in a controlled manner.
If you injure your shoulder, have chronic shoulder and arm pain, or suspect you have a rotator cuff tear, you should see your doctor. . If your doctor suspects that you have a rotator cuff injury, they'll likely order imaging tests, such as an: X . The rotator cuff is a group of muscles critical for the strength, stability and function of the shoulder. Tears of the rotator cuff tendons are a common source of shoulder pain, weakness and other problems. Imaging studies, such as radiographs, MRIs or ultrasounds, are used to evaluate rotator cuff tears. Physical therapy and the occasional use of cortisone . Welcome to the club. Rotator cuff issues are common, an unfortunate side effect from the wear and tear of daily life. More than 2 million Americans visit their doctor every year because of rotator .
spigen slim armor note 3 drop test
Diagnostic Tests for Torn Rotator Cuff. . An MRI scan enables your doctor to see the soft tissue in the shoulder and determine if you have a rotator cuff tear and whether it is partial or full thickness. An MRI can also provide doctors information about the tendon retraction or tear pattern, which may influence decisions about what surgical . Your doctor will test your range of motion and strength. . This means if you have a rotator cuff injury, your doctor is likely to first try nonsurgical methods. . Know when to see a doctor for .Occasionally, patients younger than 35 get partial tears of the rotator cuff. These tears may be associated with an injury. Partial rotator cuff tears are common in people who are overhead athletes (they play sports with an upper arm and shoulder arc over the head), such as pitchers in baseball. Partial rotator cuff tears in competitive .Rotator cuff tears are among the most common shoulder injuries. They happen when a rotator cuff tendon is separated, either partially or completely, from the bone. As you age, the risk of rotator cuff tears increases. That’s because rotator cuff tendons have a tendency to fray over time, making them even more vulnerable to damage.
The rotator cuff is a common cause of pain in the shoulder. Pain can happen because of: Tendinitis — inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons. Bursitis — inflammation of the bursa. Impingement — this happens because the space between the top of your shoulder (acromion) and the rotator cuff tendons becomes smaller when you raise your arm.Rotator cuff tears are more common in the dominant arm — the arm you prefer to use for most tasks. If you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, there is a greater likelihood of a rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder — even if you have no pain in that shoulder. Several factors contribute to degenerative, or chronic, rotator cuff tears. Urgent rotator cuff repair should be considered when acute weakness occurs after a shoulder injury, provided that shoulder ultrasound or MRI document a repairable cuff tear. Rotator cuff surgery (repair or smooth and move) should be considered in chronic rotator cuff tears that have not responded to a trial of exercise has failed to yield the .
You can't see a rotator cuff tear on an X-ray, but your doctor will be able to see other injuries to your shoulder such as arthritis or bone spurs. You may have other tests, including: (See 'Rotator cuff injury tests' above.) If tendinitis is confirmed with an imaging study, some clinicians will inject a steroid/local anesthetic mixture into the joint. . Conservative treatment is usually recommended first if you do not have a complete rotator cuff tear or are older, less active, or if there is minimal pain. Conservative .To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test. Evidence [edit | edit source] Based on the Park et al study, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator cuff .
You also can injure your rotator cuff during traumatic falls or accidents. Generally speaking, rotator cuff problems tend to produce three main symptoms: shoulder pain, decreased shoulder motion and weakness. Although most patients will have some level of each of these symptoms, not everyone with a rotator cuff tear will have all three symptoms. Rotator cuff injury is a common cause of shoulder pain, especially in older and active people. Tears can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. The cause of a rotator cuff tear can be traumatic or attritional. Treatment is typically based on degree of dysfunction, pain, quality of tendons and muscles of.
special tests for shoulder instability
WEBProfessora de inglês / cibellyferreira / cibellyferreira_ / https: instagram.com/cibellyferreira_ twitter.com/https: onlyfans.com/cibellyferreira
tests to see if you have a rotator cuff tear|how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff